いろいろ normal sinus rhythm with bundle branch block 504508-Normal sinus rhythm incomplete right bundle branch block borderline
Sinus Rhythm means you heart is beating at a steady consistent rate A first degree AV block means that the electrical signal that starts in the Atria (upper chambers) of the heart and is relayed to the Ventricles (lower chambers) of the heart, is taking too long to get there It's sometimes referred to on the EKG as a prolonged PR timeJul 16, 09 · I will help you with your question Overall, your heart is beating correctly (sinus rhythm) with some additional beats (premature atrial complexes) these are common and are not worrisome The right bundle block, left posterior fascicular block, and bifascicular do show that there is some damage or abnormality of the conduction system of the heart11 conduction between the atrium and His bundle at right atrial pacing cycle lengths of less Figure 3 Atrial flutter with 21 atrioventricular block and left bundle branch block aberration was induced in Patient 4, who had been referred for runs of nonsustained ventricular

Alternating Bundle Branch Block Circulation
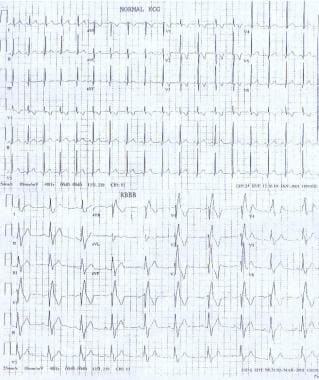
Normal sinus rhythm incomplete right bundle branch block borderline
Normal sinus rhythm incomplete right bundle branch block borderline-Please can somone clarify further many thanksJun , 18 · The bundle of His is an area of the heart that conducts impulses to the left and right ventricles Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is a blockage of




B Normal Sinus Rhythm Left Bundle Branch Block With Anterolateral T Download Scientific Diagram
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm ECG (Example 1) If action potentials do not go through the normal LAFB to the left ventricular myocardium toIf the QRS duration is ≥0,110 seconds butJul 26, 18 · These electrocardiographs demonstrate a normal sinus rhythm and a sinus rhythm with a right bundle branch block Anatomy of the penetrating portion of the atrioventricular (AV) bundle is shown This image depicts the electrophysiologic events of right bundle branch block
CHRONIC bifascicular bundle branch block or left bundle branch block (LBBB) can progress to complete heart block (CHB) with the risk of sudden perioperative death 1–3 In the perioperative period, different factors can induce a prolongation of atrioventricular (AV) conduction and increase the risk for bradyarrhythmiasBundle Branch Block First Degree AV Block Junctional Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Second Degree AV Block, Type 2 Normal sinus rhythm with multifocal PVCs Which rhythm is this?Feb 03, 13 · Sinus Rhythm With Left Bundle Branch Block, PVCs, and Fusion Beats This is a great ECG for teaching your students about some of the different causes of wide QRS This year old man has a sinus rhythm that is around 100 bpm, and his QRS is widened at 148 ms (148 sec)
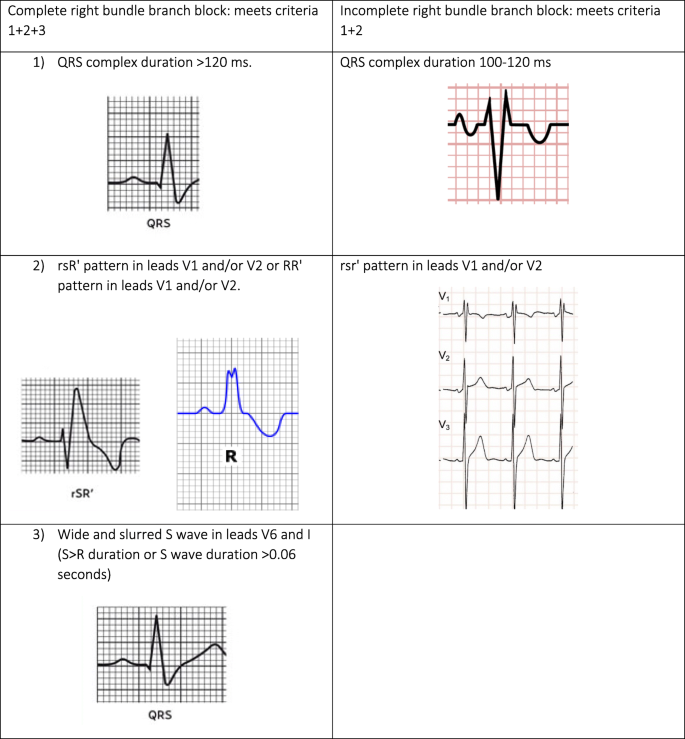
Oct 01, 1971 · Right bundle branch block with normal, (AH) and HisPurkinje system (HV) were measured during normal sinus rhythm and atrial pacing In all but four patients with sinus rhythm in whom second degree AV block developed only during atrial pacing at rapid rates (range 100 to 180/minute) the block was localized in the AH interval (AV node)Figure 1 These ECGs show the difference between normal conduction, left bundle branch block (LBBB) and right bundle branch block (RBBB) As evident from these ECGs, the cardinal difference between normal conduction and bundle branch blocks is the QRS duration bundle branch blocks are caused by dysfunctional bundle branches, which results in slow (and abnormal) activation ofMar , 21 · Incomplete Right Bundle Branch Block in Pediatric Population The rsr', rsR', or rSR' pattern with a normal QRS duration in V1 and V2 is a normal variant in children of any age 2 3 Incomplete right bundle branch block is defined by QRS complex duration between 90 and 100 ms in children between 4 and 16 years of age, and between 86 and 90 ms in children less than 4




Treatment Of Painful Left Bundle Branch Block Syndrome With Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Or Right Ventricular Pacing Heartrhythm Case Reports




Marked Sinus Bradycardia Associated With Remdesivir In Covid 19 A Case And Literature Review Jacc Case Reports
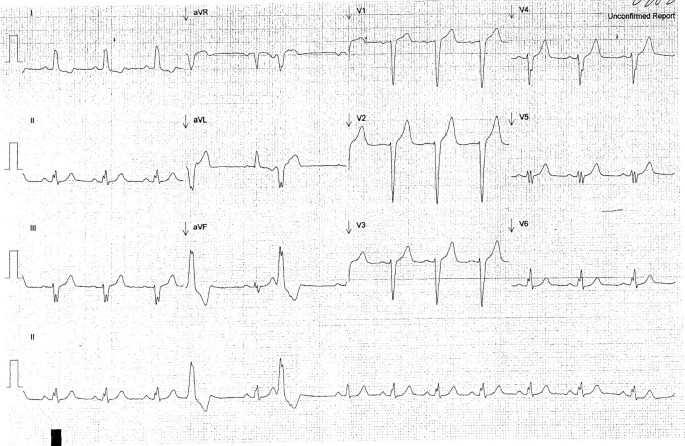
Results The ECG during sinus rhythm showed right bundle branch block, normal QT interval and persistent ST segment elevation in precordial leads V1 to V2V3 not explainable by electrolyte disturbances, ischemia or structural heart disease No histologic abnormalities were found in the four patients in whom ventricular biopsies were performedJun 23, 21 · PDF On Jun 23, 21, Syed M Saad and others published A Case of Intermittent Left Bundle Branch Block Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGateHave taken second time and ECG both attachedPlease suggest 724 Views v



Severe Myocardial Ischemia In A Patient With Diabetes Mellitus And Left Bundle Branch Block Springerlink




Case B12 Junctional Rhythmn With Right Bundle Branch Block St Emlyn S Ecg Library St Emlyn S
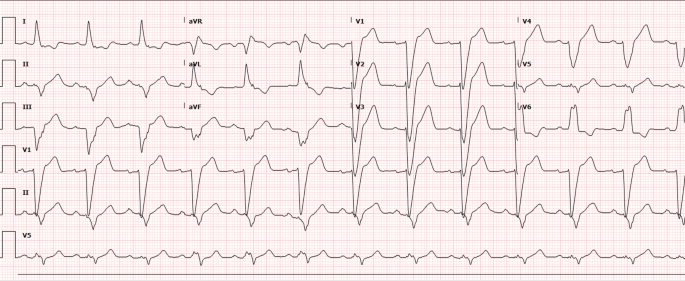
Normal Sinus Rhythm Incomplete right bundle branch block Borderline ECG Is this more serious?Ventricular trigeminy is a sinus rhythm that occurs when every third beat is a premature ventricular contraction (PVC) Table 1 ECG Characteristics 2Jun 13, 16 · The electrical impulse in bundlebranch block originates in the sinus node, not in ventricular tissue, but a discussion of bundlebranch block is included in this rhythm group because of the location of the block within the ventricles and the wide QRS complex



Ecg Abnormalities Almostadoctor



Right Bundle Branch Block Thoracic Key
Normal sinus rhythm Possible left atrial enlargement Incomplete right bundle branch block borderline ECG Ventrate 77 bpm PR interval 156ms QRS duration 106 ms QT/QTc 398/450 ms PRT axes 73 72 52 40HZ 250 mm/mV 4 by 25s 1 rhythm ld MAC55 009A 12SL TM VFascicular block involves the anterior or posterior fascicle of the left bundle branch Interruption of the left anterior fascicle causes left anterior hemiblock characterized by modest QRS prolongation (< 1 millisecond) and a frontal plane QRS axis more negative than − 30 ° (left axis deviation)Left posterior hemiblock is associated with a frontal plane QRS axis more positive than 1 °Alternation of right (RBBB) or left (LBBB) bundle branch block with normal conduction, known as 21 bundle branch block, 101 may be tachycardia or bradycardia dependent 104 The most common type of alternans is between the left bundle branch pattern and either a normal or left ventricular hypertrophy pattern (Figure 2413)



Lbbb Ecgpedia




Diagnosis Of Acute Myocardial Infarction In Left Bundle Branch Block Semantic Scholar
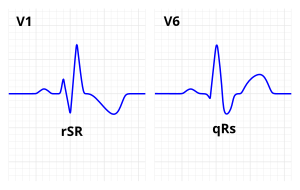
Feb 08, 18 · Sinus Rhythm There is an rSR' in V1, with wide Swaves in lateral leads (right bundle branch block, RBBB) Normally, RBBB has a bit of ST depression in V1V3 that is discordant (in the opposite direction of) the R'wave So that bit of ST Depression in V1 is normalJan 02, 18 · Normal sinus rhythm Normal sinus rhythm is defined as the rhythm of a healthy heart It means the electrical impulse from your sinus node is being properly transmitted In adults, normal sinusRight bundle branch block comes from a problem with the heart's ability to send electrical signals It usually doesn't cause symptoms unless you have some other heart condition Your heart has 4 chambers The 2 upper chambers are called atria, and the 2 lower chambers are called ventricles In a healthy heart, the electrical signal to start



Diagnosis Of Right Bundle Branch Block A Concordance Study Bmc Family Practice Full Text
/right-bundle-branch-block-rbbb-1745785-FINAL-35a6f733fab44ef08240c21a675c12da.png)



Bundle Branch Block Overview And More
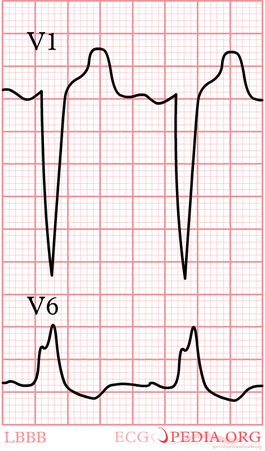
Jun 02, · These electrocardiographs demonstrate a normal sinus rhythm and a sinus rhythm with a right bundle branch block Anatomy of the penetrating portion of the atrioventricular (AV) bundle is shownThe delay or block can happen on the pathway that sends electrical signals to either the left or right side of the ventricles The blockages can be seen as a particular pattern on an ECG There are two types of bundle branch blocks Left bundle branch block which could be a sign of an underlying heart condition which you may need treatment forFeb 17, 15 · This ECG shows a "classic" left bundle branch block pattern The ECG criteria for left bundle branch block are · Wide QRS (12 seconds or greater) · Supraventricular rhythm (ventricular rhythms do not travel via the LBB) · The QRS in V1 is negative, and the QRS in Leads I and V6 are positive The left bundle branch (LBB) can be blocked permanently, temporarily,
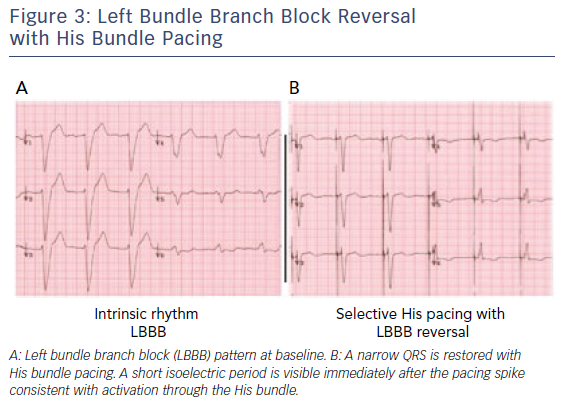



His Bundle Pacing A New Frontier In The Treatment Of Heart Failure Aer Journal



64 Year Old Female Cc Trouble Breathing Conclusion Ems 12 Lead
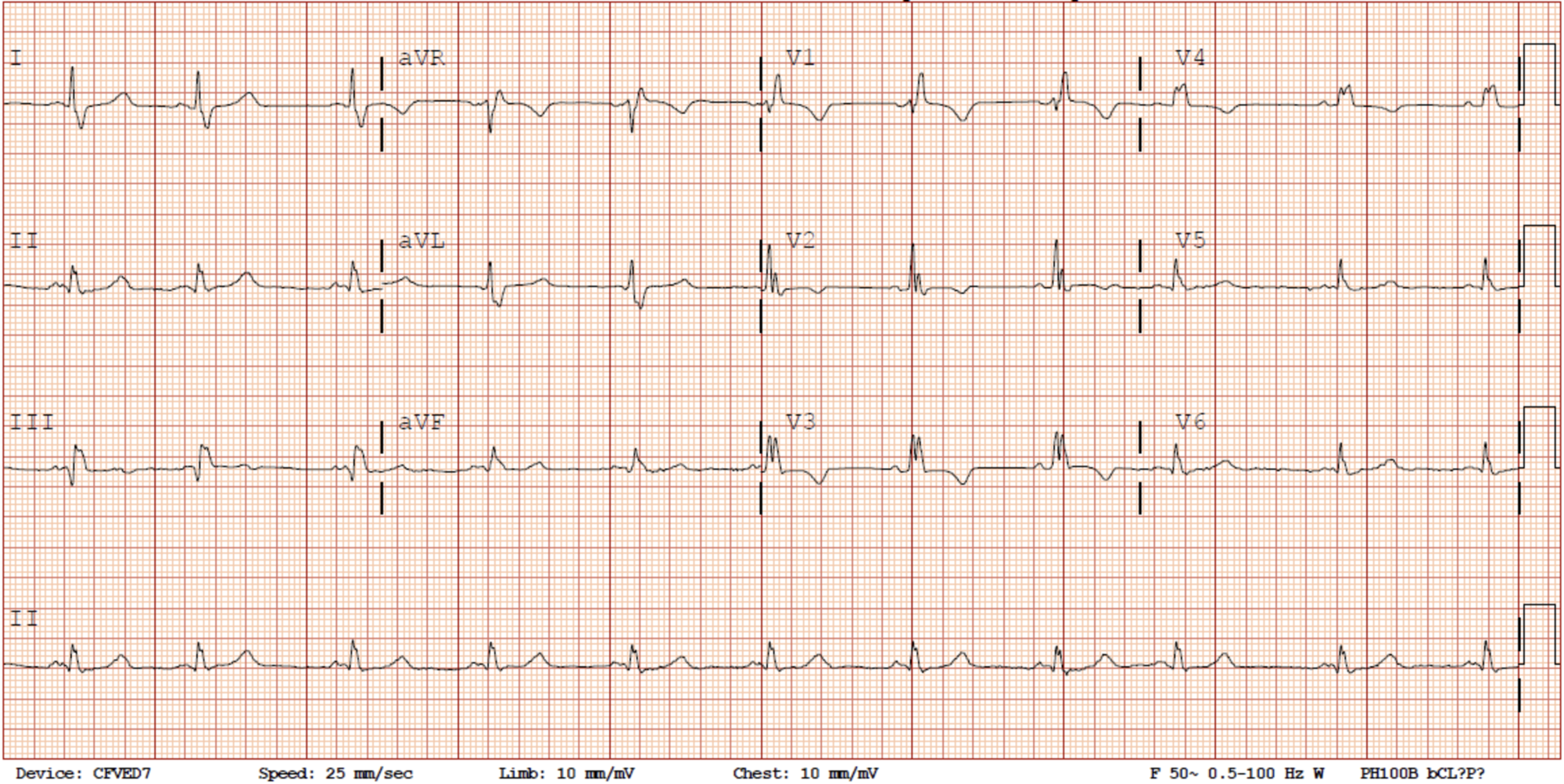
From a sinus rhythm at 90 bea~min to 98 beats/min, with a change in conduction from normal to a left bundle branch pattern Conduction became normal transiently with carotid massage During the re mainder of the case, the conduction varied between the left bundle branch pattern and the normalSinus rythm with marked sinus arythmia incomplete right bundle branch block Borderline ECG ECG results 79 pbm, Pr interval 152 ms, Qrs duration 100 ms,QT/QTc 352/403 ms, p r t axes 21 17 Is this something I should be worried about?Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB) ECG Review;




B Normal Sinus Rhythm Left Bundle Branch Block With Anterolateral T Download Scientific Diagram




Right Bundle Branch Block Rbbb Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis
Normal sinus rhythm Regular Rate P Wave Present, upright PR Interval 01 sec QRSAug 07, 13 · There is sinus rhythm and Right Bundle Branch block There is a tall Rwave in V2 and V3 and slightly excessive ST depression in lead V2, with a biphasic wavePremature atrial complex with noncompensatory pause




Ventricular Arrhythmias And Bundle Branch Block Flashcards Quizlet
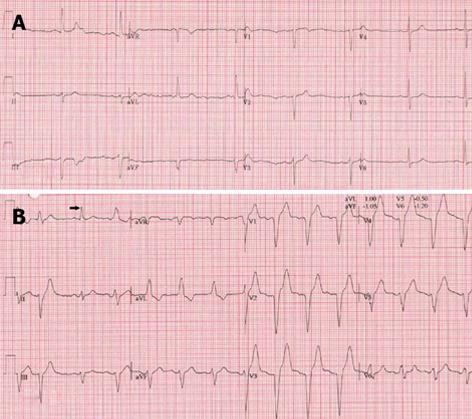



Exercise Induced Left Bundle Branch Block An Infrequent Phenomenon Report Of Two Cases
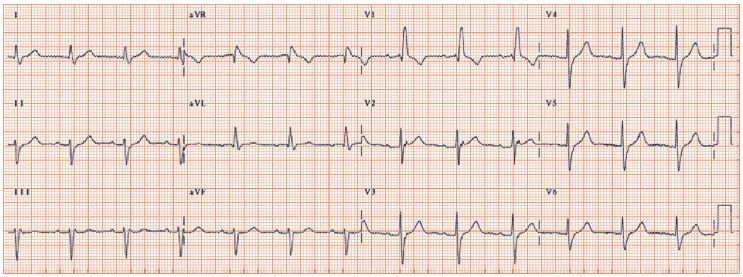
Sinus rhythm with right bundle branch block (RBBB) and the echocardiogram was normal He underwent a 24hour Holter study, one of the tracings of which is shown in Figure 1 What does it reveal and what is the underlying mechanism of the finding?Normal sinus rhythm with unifocal PVCs Which rhythm is this?Ratedependent bundle branch block can revert to sinus rhythm at critical heart rate11 The transition from normal to abnormal may occur by alterations in heart rate by only 1 or 2 beats/min10 This critical heart rate is dependent on change in heart rate3 With rapid decrease in heart rate, sinus rhythm may




Left Bundle Branch Block Induced Cardiomyopathy In A Transplanted Heart Treated With His Bundle Pacing Jacc Case Reports



Chest Pain Left Bundle Branch Block And Excessively Discordant St Segment Elevation Ems 12 Lead
In normal sinus rhythm, a resting heart rate of below 60 bpm is called bradycardia and a rate of above 90 bpm is called tachycardia Incomplete right or left bundle branch block;Jun 07, 16 · Wiring of heart Sinus rhythm means that the electrical activity that controls the contraction of the heart, starts in the sinus node Right bundle branch block means that the right bundle (part of the electrical wiring) does not conduct the impulse which changes the appearance of the ekg Right bundle branch block as opposed to left bundle branch block is usually benignLows AH intervals during sinus rhythm of less than or equal to 60 ms;



Figure 1 Ecg Showing Normal Sinus Rhythm Normal Qrs Duration And Left Ventricular Hypertrophy Significant Pr Prolongation And New Onset Left Bundle Branch Block In Aortic Root Abscess A Marker Of
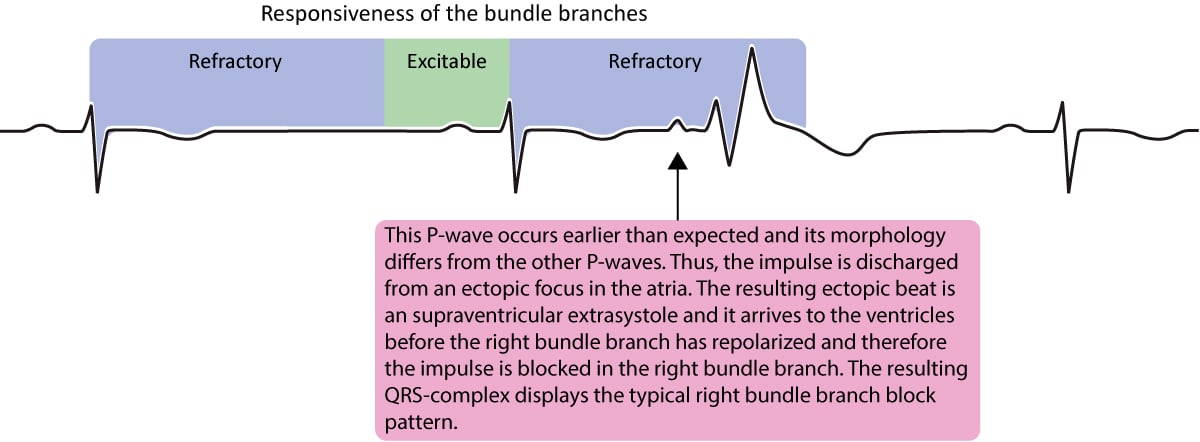



Aberrant Ventricular Conduction Aberrancy Aberration Ecg Echo
Bifascicular block Bifascicular block is a conduction delay or "block" below the atrioventricular (AV) node in two of the three fascicles (the right bundle branch and left anterior and left posterior fascicles of the left bundle branch) Right bundle branch block (RBBB) is typically combined with either left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) or left posterior fascicular block (LPFB) 1)Apr 23, · CRT should now be strongly considered in any patient with heart failure and bundle branch block As we have seen, bundle branch block causes the ventricles to beat sequentially (one after another) instead of simultaneously This discoordination of the normal pattern of ventricular contraction diminishes the efficiency of the heart beatJun 14, 17 · The ECG strip below shows normal sinus rhythm, then atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response develops With the faster heart rate, the QRS complex morphology changes to




Right Bundle Branch Block Rbbb Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Right Bundle Branch Block Wikipedia
Nonspecific intraventricular conduction delay (IVCD) Some cases of left anterior or posterior fascicular block ;In left bundle branch block (LBBB), the QRS duration is greater than or equal to 1 ms in adults, there is broad notched or slurred R wave in leads I, aVL, V5 and V6 The STsegment and T waves are usually opposed to QRS directionOct 01, · A 68yearold gentleman without any comorbidities presented with recurrent syncope His baseline ECG showed sinus rhythm with right bundle branch block (RBBB) and the echocardiogram was normal He underwent a 24hour Holter study, one of the tracings of which is shown in Figure 1 What does it reveal and what is the underlying mechanism of the



1




Alternating Bundle Branch Block Circulation
Rhythm analysis indicates a borderline normal sinus rhythm (NSR) Also present is a right bundle branch block (RBBB) Premature Atrial Complexes (PACs) exist in this encounter as well This encounter shows a borderline regular rhythm and heart rate, displaying P wavesThe determination that a bundle branch block (often referred to as BBB) exists is made by reviewing a patient's EKG In the presence of a bundle branch block, the QRS is wider than its normal value of 0410 seconds and will typically be 1216 seconds In bundle branch block, only one of the ventricles is directly caused to contract by theJul 19, 16 · ECG Features Figure 1 ECG Strip 1 A normal sinus rhythm has a normal heart beat with respect to rhythm and rate Table 1 ECG Characteristics 2




B Normal Sinus Rhythm Left Bundle Branch Block With Anterolateral T Download Scientific Diagram
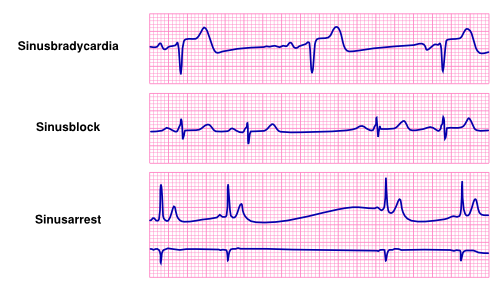



Bradycardia Textbook Of Cardiology
Right bundle branch block comes from a problem with the heart's ability to conduct electrical signals It usually doesn't cause symptoms unless you have some other heart condition Your heart has 4 chambers The 2 upper chambers are called atria The 2 lower chambers are called ventricles In a healthy heart, the electrical signal for yourOct 11, 19 · A 38yearold woman not on regular medications presented with a history of intermittent palpitations Her 12lead electrocardiogram (ECG) showed sinus rhythm with PR interval of 160 ms, QRS of 140 ms duration, and left bundle branch block (LBBB) patternAn echocardiogram demonstrated a structurally normal heartMay 25, 18 · These electrocardiograms show a normal sinus rhythm and a sinus rhythm with a left bundle branch block View Media Gallery LBBB in children is associated with cardiovascular disease, surgery, or ablation within the left ventricle and is not observed in the general population



Pediatric Right Bundle Branch Block Background Pathophysiology Etiology



Unusual Source Of Tachycardia In An Adolescent International Journal Of Emergency Medicine Full Text




Ecg Amboss



Right Bundle Branch Block Part 1 Ems 12 Lead




Intermittent Left Bundle Branch Block What Is The Mechanism




A Normal Sinus Rhythm Left Axis Deviation And Left Bundle Branch Block Download Scientific Diagram



Cureus Transient Right Bundle Branch Block Resulting From A Blunt Cardiac Injury During A Motor Vehicle Accident



Ecg A Pictorial Primer



1



Bundle Branch Block Wikipedia



Right Bundle Branch Block Wikipedia



1



Ecg A Pictorial Primer




View Image




Bundle Branch Blocks
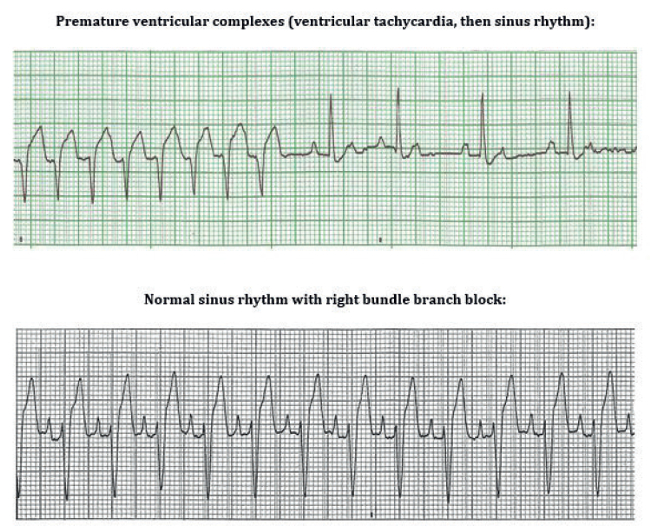



Clinical Approach To Arrhythmias Wsava 15 Congress Vin




B24 Right Bundle Branch Block With The Wenckebach Phenomenon In Acute Myocardial Infarction St Emlyn S




Left Bundle Branch Block Lbbb Ecg Criteria Causes Management Ecg Echo
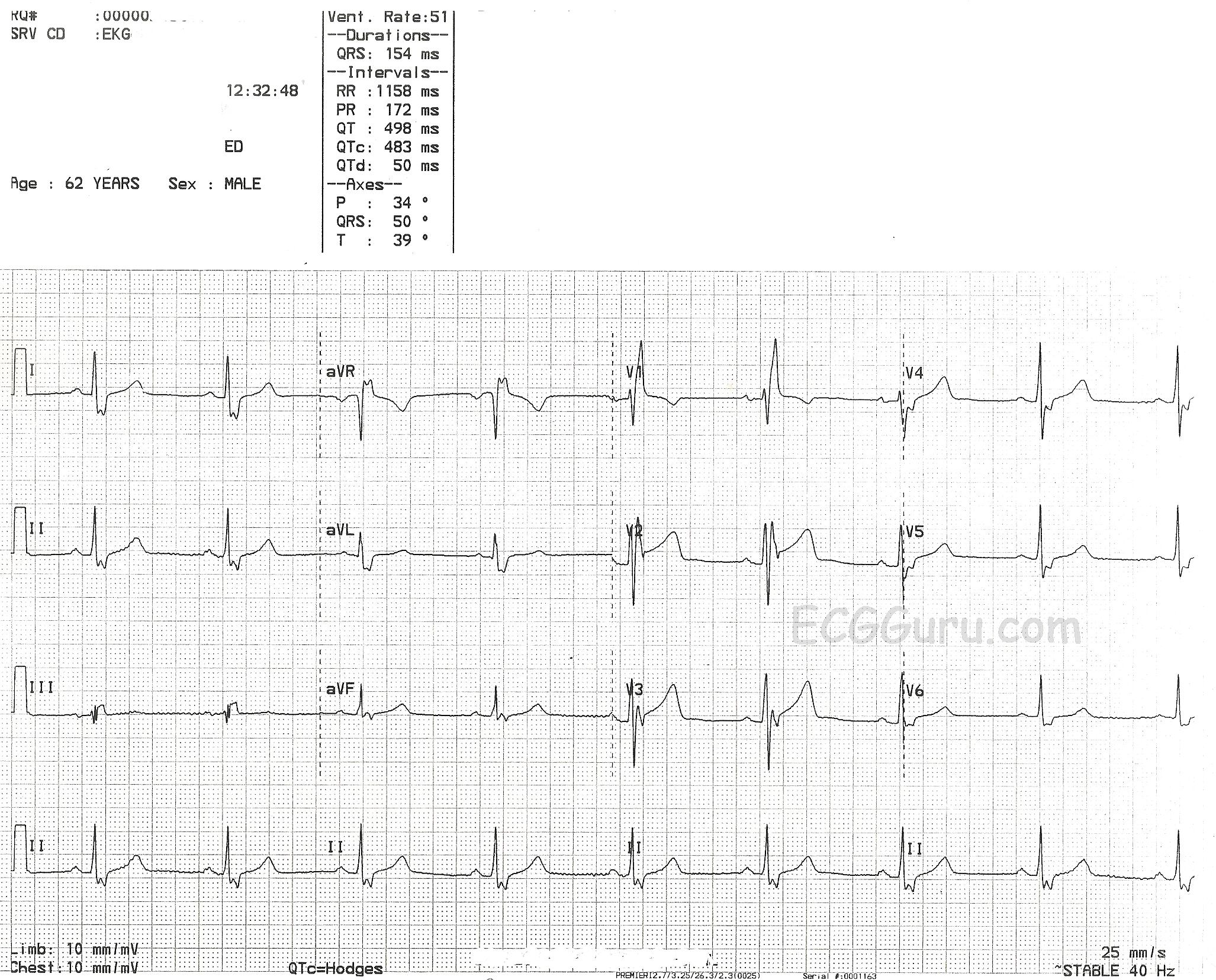



Right Bundle Branch Block Ecg Guru Instructor Resources



Heart Rhythm Guide




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog New Left Bundle Branch Block Lbbb And Dyspnea




Rate Related Left Bundle Branch Block And Cardiac Memory In A Patient With Bradycardia Case Report And Literature Review Seibolt 18 Clinical Cardiology Wiley Online Library



Complete Right Bundle Branch Block Of Unique Behavior What Is The Mechanism Akerstrom Cardiology Journal



Ecg A Pictorial Primer



Complete Right Bundle Branch Block Of Unique Behavior What Is The Mechanism Akerstrom Cardiology Journal




A Normal Sinus Rhythm With Left Bundle Branch Block Download Scientific Diagram
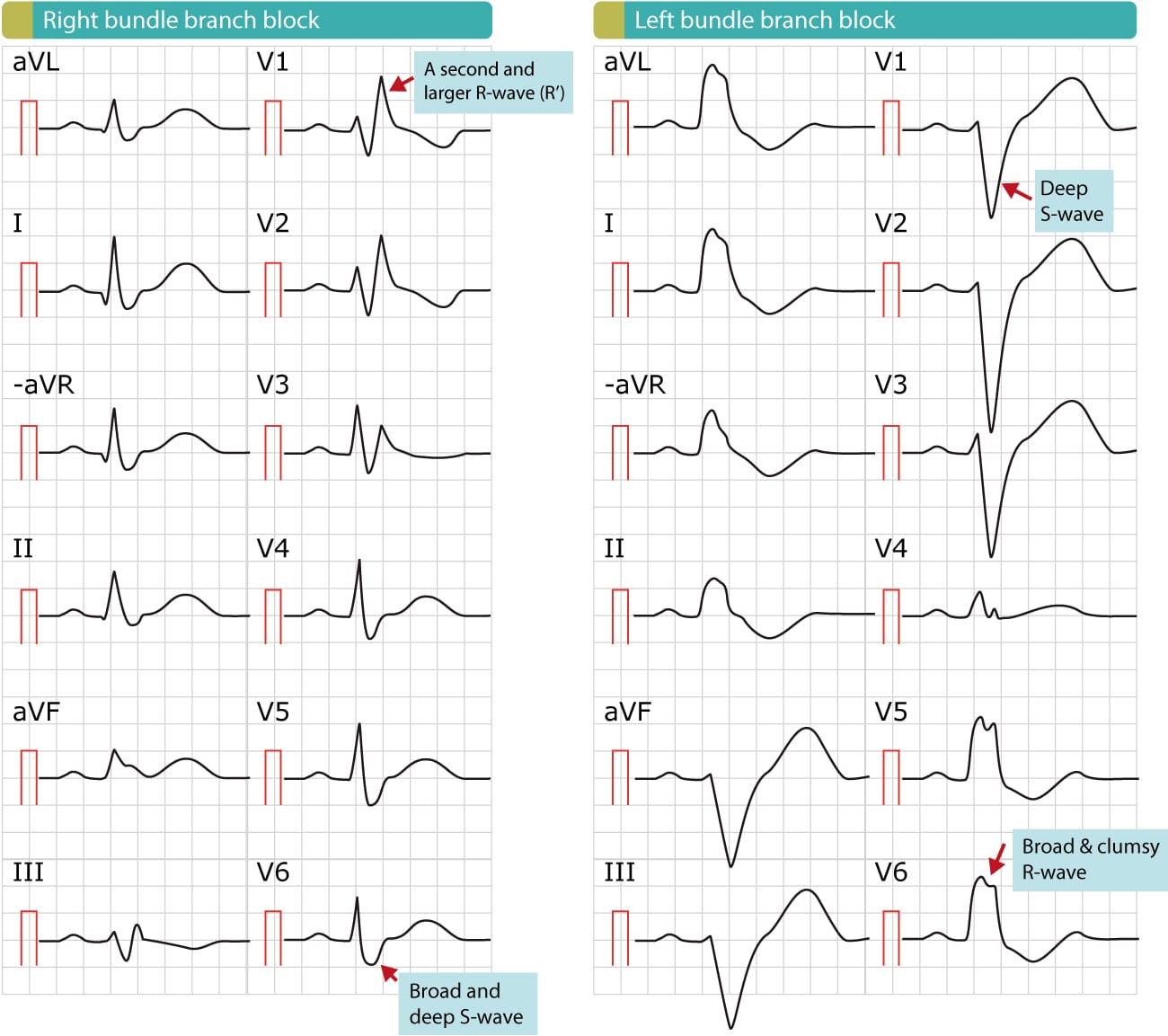



Right Bundle Branch Block Rbbb Ecg Criteria Definitions Causes Treatment Ecg Echo




Resolution Of Bundle Branch Block Circulation
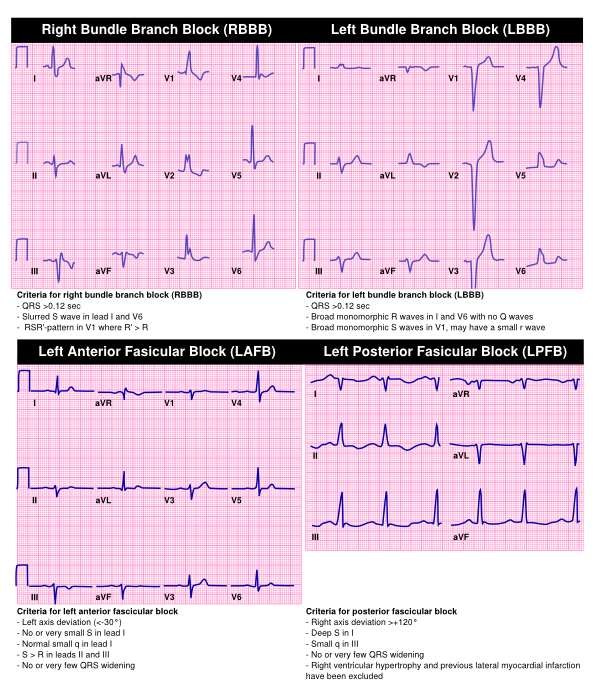



Bradycardia Textbook Of Cardiology




Pin On Ecg Self Assesment




In Patients With Left Bundle Branch Block What S The Best Test For Cad Consult Qd
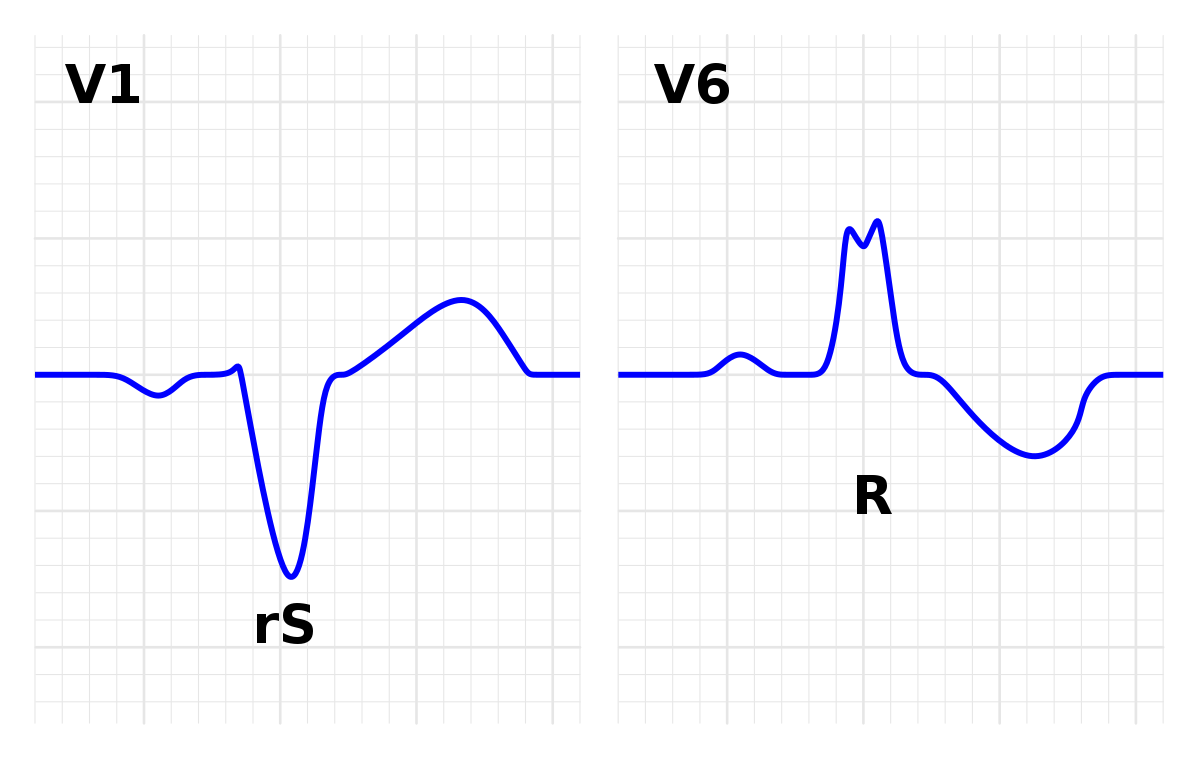



Left Bundle Branch Block Wikipedia




B26 Left Bundle Branch Block Lbbb Ecgs At St Emlyn S




Ekg S Internal Medicine University Of Nebraska Medical Center
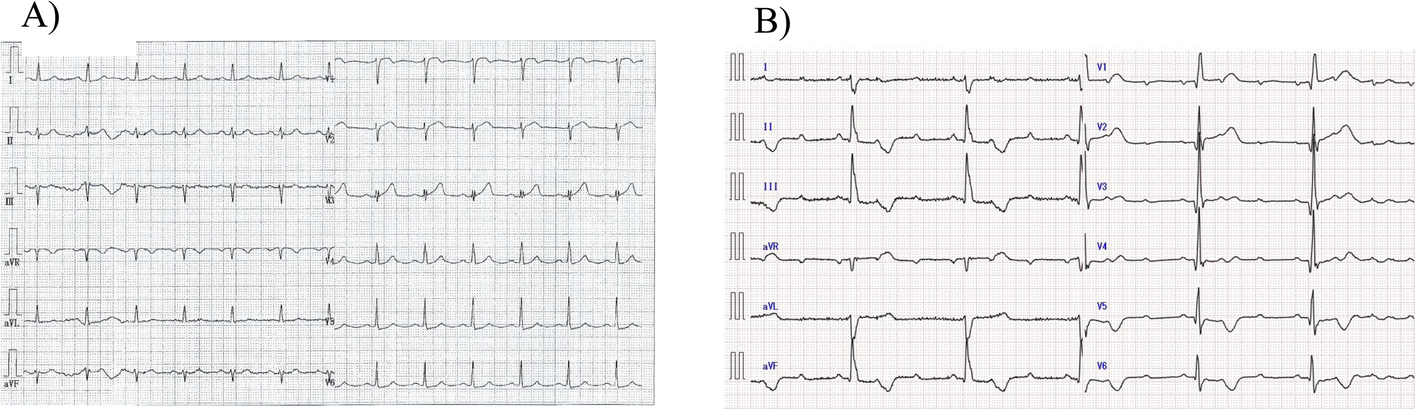



Figure 1 Consecutive Electrocardiographic Changes During Percutaneous Coronary Intervention For Acute Coronary Syndrome With High Grade Atrioventricular Block A Case Report Springerlink




Right Bundle Branch Block Ekg Examples Wikidoc




The Heart Remembers Anterior T Wave Inversions In A Patient With Intermittent Left Bundle Branch Block




Second Degree 2 1 Atrioventricular Block With Right Bundle Branch Block What Is The Mechanism Heart Rhythm




A Normal Sinus Rhythm Left Axis Deviation And Left Bundle Branch Block Download Scientific Diagram




View Image
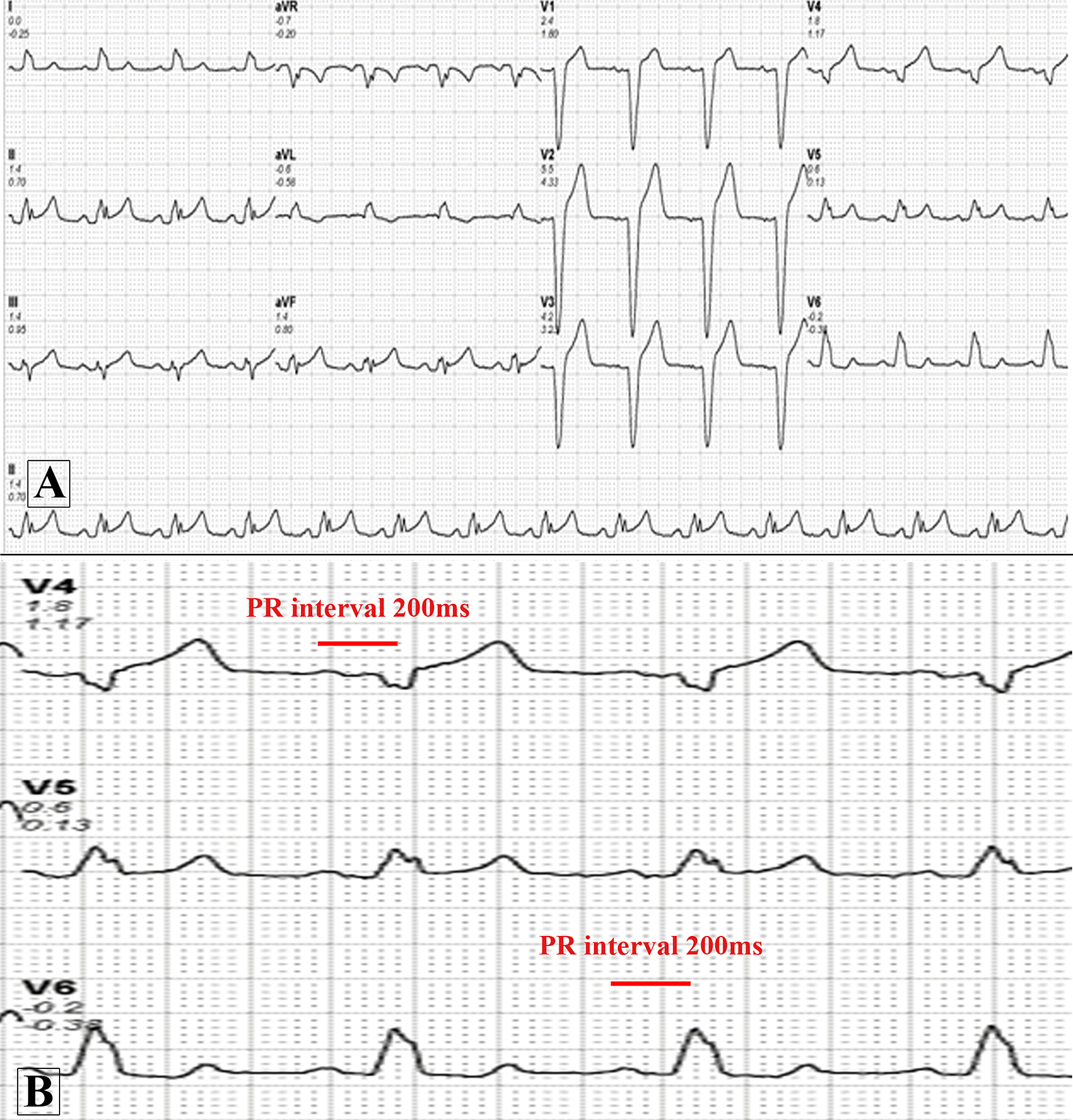



Cureus A Curious Case Of Intermittent Left Bundle Branch Block Associated With Cough
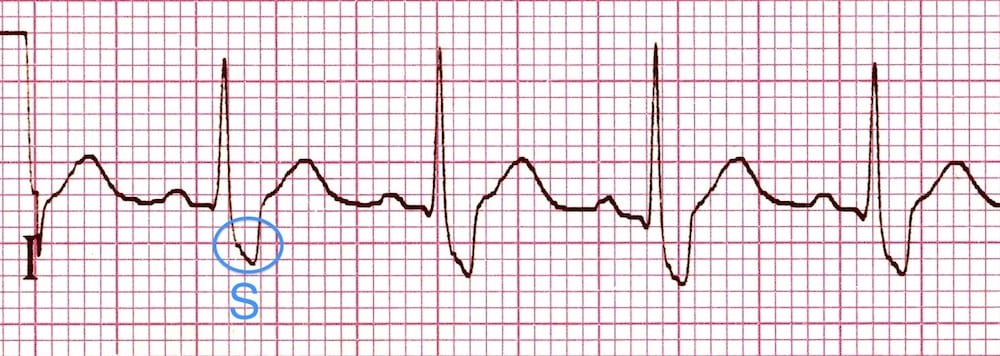



Right Bundle Branch Block Rbbb Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Intermittent Left Bundle Branch Block A Diagnostic Dilemma



Bifascicular Blocks What You Need To Know Ecg Medical Training
/Bundle-Branch-Block-58960e843df78caebceafb79.jpg)



Bundle Branch Block Overview And More




Right Bundle Branch Block In Acute Coronary Syndrome Diagnostic And Therapeutic Implications For The Emergency Physician The American Journal Of Emergency Medicine




Ecg Amboss




Practical Electrocardiography Bundle Branch Block Scott Ewing D




Transient Disappearance Of Left Bundle Branch Block Pattern An Unusual Ecg Presentation Of Acute Pulmonary Embolism Postgraduate Medical Journal



Differential Diagnosis Of Tachycardia With A Typical Left Bundle Branch Block Morphology




Electrocardiogram Demonstrating Normal Sinus Rhythm With First Degree Download Scientific Diagram




County Em Rhythm Nation Ecg Intermittent Left Bundle Branch Block



Figure 1 Ecg Normal Sinus Rhythm Mild Tachycardia At 102 Beats Per Minute Right Axis Deviation Poor R Wave Progression Right Ventricular Hypertrophy And Right Bundle Branch Block Signs Of Right Ventricular Strain
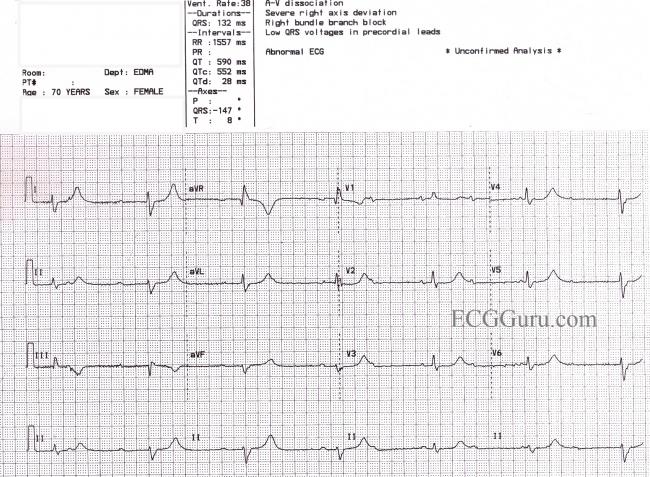



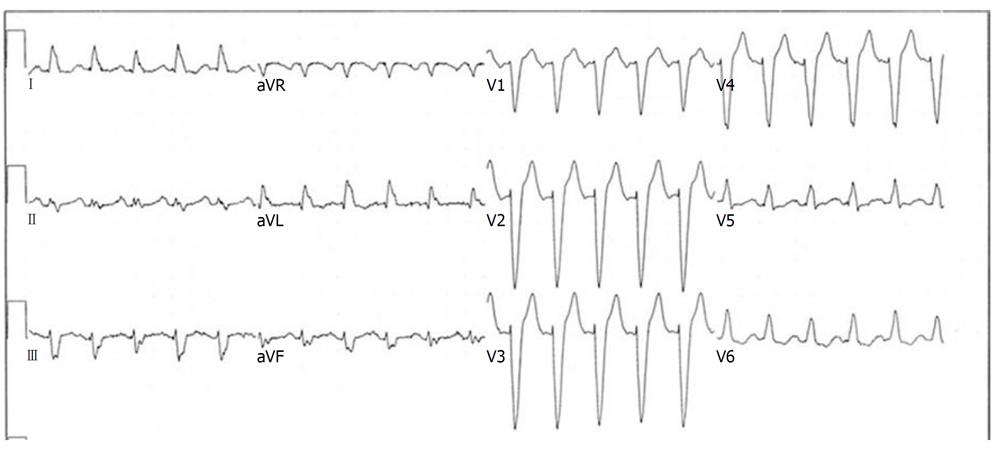
Third Degree Av Block And Junctional Escape Rhythm With Right Bundle Branch Block And Prolonged Qtc Interval Ecg Guru Instructor Resources
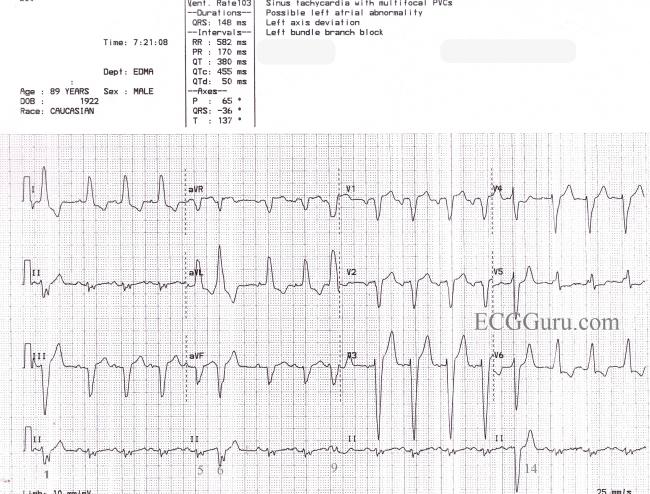



Sinus Rhythm With Left Bundle Branch Block Pvcs And Fusion Beats Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Resolution Of Bundle Branch Block Circulation



Bundle Branch Block
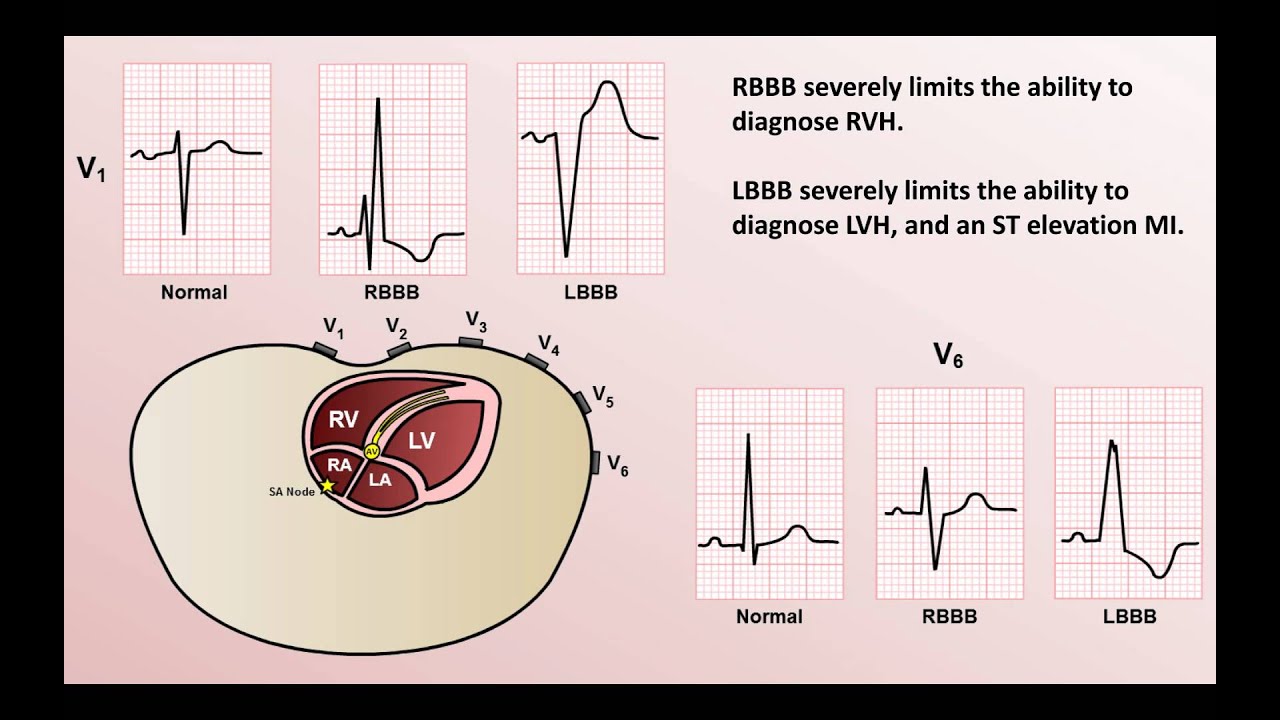



Intro To Ekg Interpretation Bundle Branch Blocks Youtube



Category Bundle Branch Block




B Sinus Rhythm Left Axis Deviation Left Bundle Branch Block Download Scientific Diagram



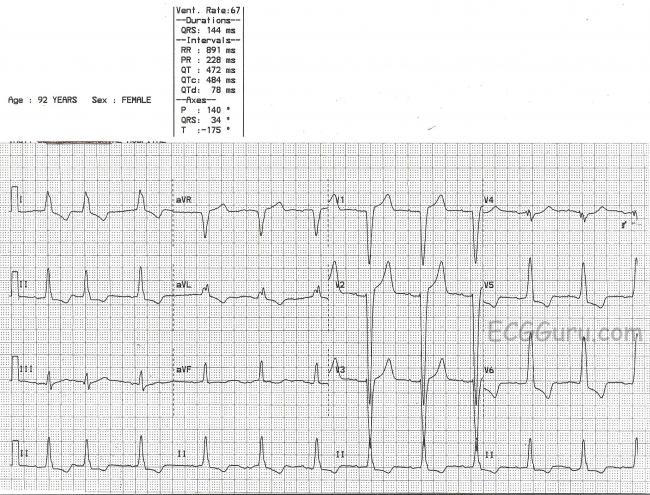
Tutorial Bundle Branch Blocks




Left Bundle Branch Block Ecg 4 Learntheheart Com




Bundle Branch Block Wikipedia




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog What Is The Rhythm And Is There New Left Bundle Branch Block Lbbb




New Human Physiology Ch 11 Bundle Branch Block Icu Nursing Nurse




Ekg Interpretation




Unusual Cause Of Acquired Rbbb Bmj Case Reports



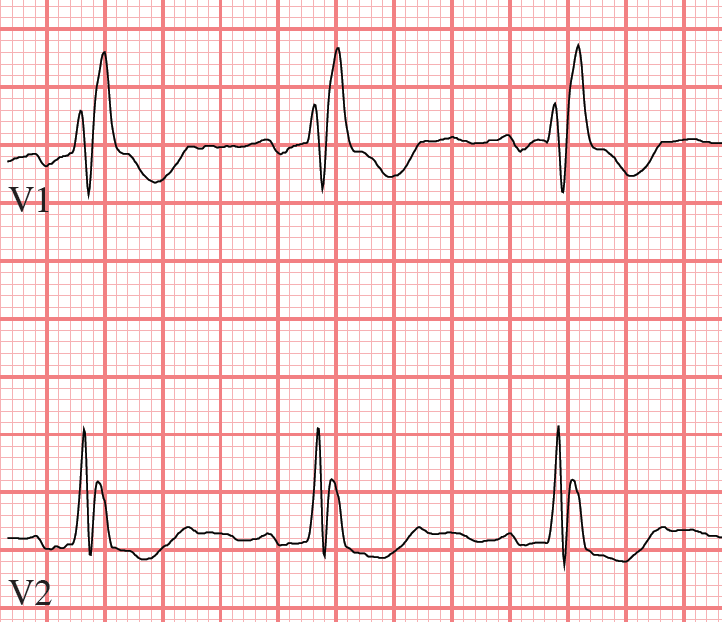
Left Bundle Branch Block Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Pdf The Rate Dependent Bundle Branch Block Transition From Left Bundle Branch Block To Intraoperative Normal Sinus Rhythm Semantic Scholar
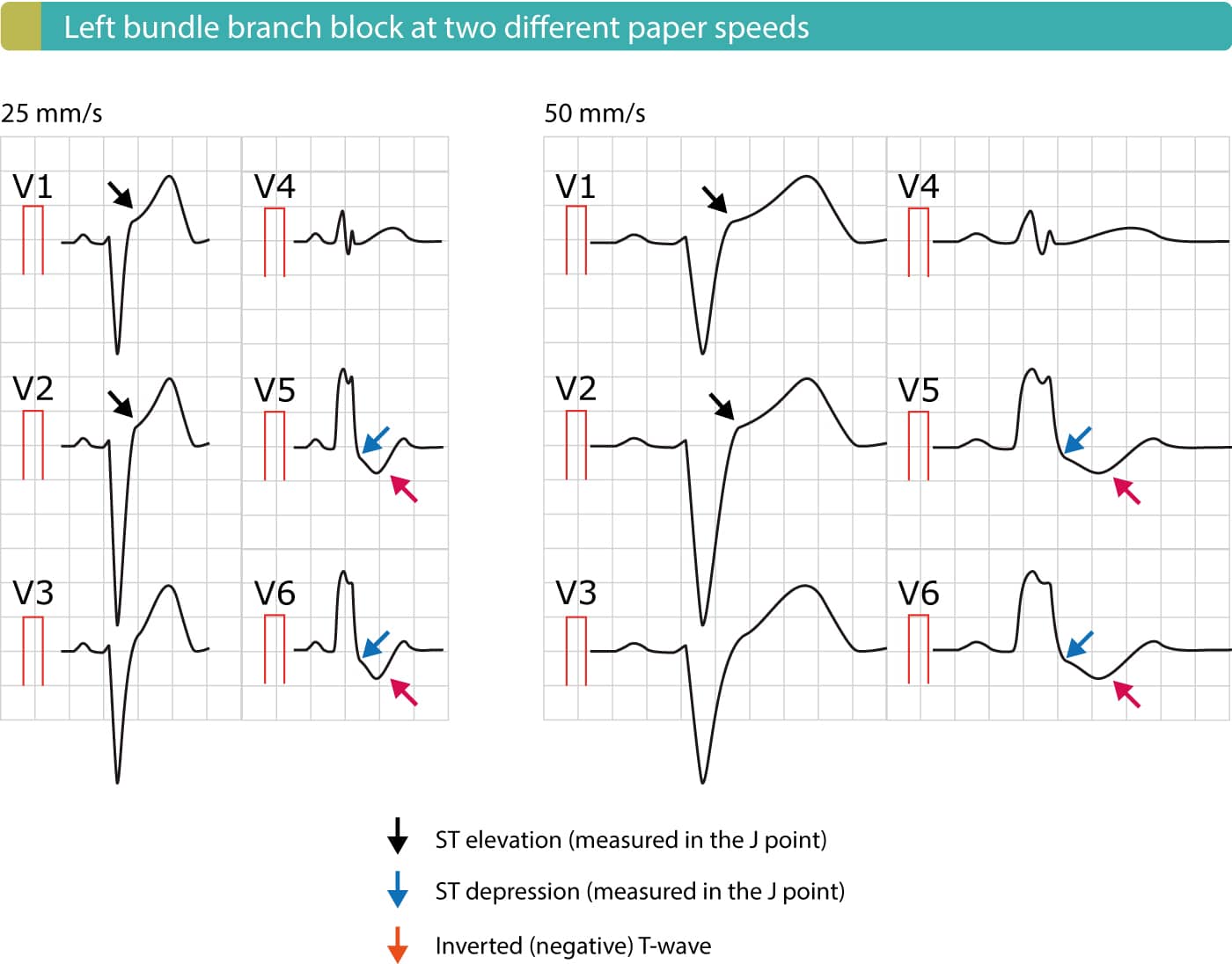



Left Bundle Branch Block Lbbb Ecg Criteria Causes Management Ecg Echo




View Image




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog What Is Lurking Underneath This New Right Bundle Branch Block
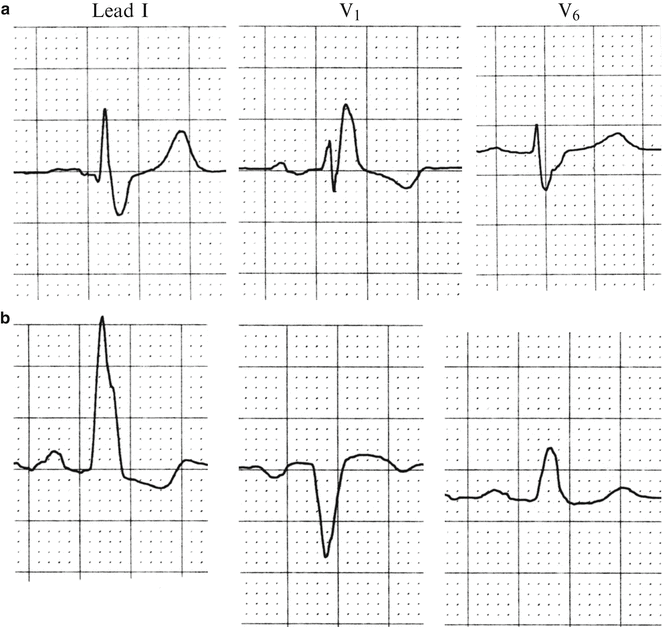



Bundle Branch Blocks And Hemiblocks Thoracic Key
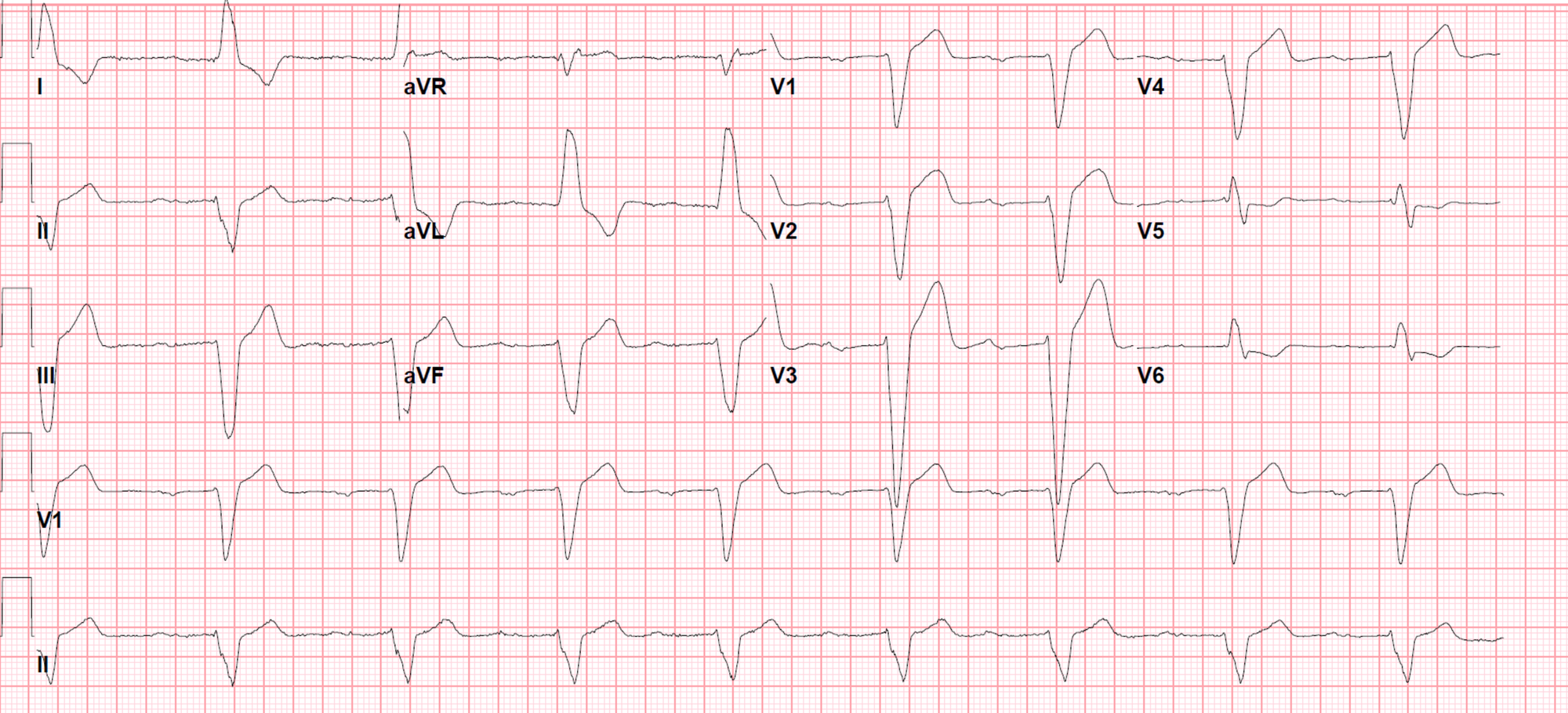



Cureus Left Bundle Branch Block A Reversible Pernicious Effect Of Lacosamide



1




The Heart Remembers Anterior T Wave Inversions In A Patient With Intermittent Left Bundle Branch Block




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog What Is The Rhythm And Is There New Left Bundle Branch Block Lbbb
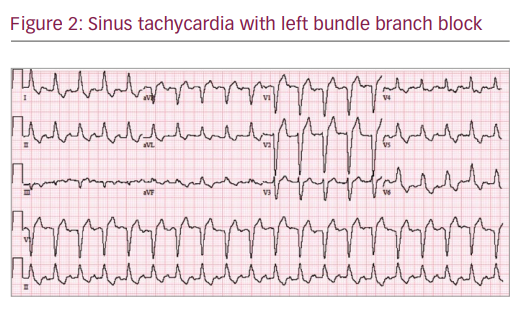



Intermittent Left Bundle Branch Block A Challenging Case Of Rare Electrocardiogram Phenomenon Touchcardio


コメント
コメントを投稿